Production of Environment Friendly Biodiesel Fuel from Fish Waste
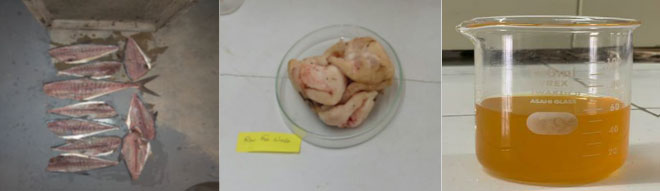
Due to the damaging impacts of fossil fuels combustion to the environment by the accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHG’s) in the atmosphere, there is global interest in developing sustainable and renewable biofuels (such as biodiesel for diesel engines) to reduce carbon dependency. The biodiesel also helps in the reduction of disaster risk through the emissions of less harmful gases as compared to fossil fuels generating carbon dioxide, which is the main contributor to climate change and global warming. Aquaculture in Pakistan is becoming a sight of attention for the private and government sectors. According to statistics, Pakistan has many marine and inland fishery resources, which produces 1 million tons of fish annually, including 0.7 million tons from sea and 0.3 million tons from inland fish farms. These fish are consumed well but their waste is unable to be managed properly. Approximately fish contains 25% to 35% of waste which comes to approximate around 350,000 tons per year and can obtain 105,000 tons of fish oil (approx. 30% by weight). If this waste is disposed of in sea marine environment causes environmental concerns associated with disposal of fish wastes into ocean waters such as reduced oxygen levels in the seawaters at the ocean bottom, burial or stifling of aquatic organisms and spreading pathogenic infections from putrefying organic matter. Therefore, fish waste is considered as a potential feedstock that can be converted into biodiesel, which also contributes to a clean energy and healthy marine eco-system in compliance with UN SDG’s (GOAL 7: Affordable and Clean Energy and GOAL 14: Life Below Water). If biodiesel conversion yield is 70% from the fish oil, then 73,500 tons of biodiesel can be produced per year. Pakistan’s total import of mineral diesel is 713000 tons/ year having import budget of USD 17.3 billion / year. Blending 10% biodiesel with mineral diesel can save a foreign exchange of USD 1.7 billion dollars. The total production cost of fish waste biodiesel was between Rs. 225 to 230 /litre as compared to selling price of mineral diesel Rs. 235 /litre. Utilization of solar energy can further reduce its production cost. Waste management has become an essential requirement to keep environment clean.
(a) Raw fish waste (b) Fish bones and (c) Extracted fish oil (from left to right)
Extraction of Bio-Active Compounds from the processing of Shrimp waste

The extraction of valuable biopolymer material from biodegradable natural resources have acquired focus due to increase growing concerns about environment. Industrial wastes and agriculture wastes are produced in huge amount, along with it agro-waste and marine wastes are significant contributor in waste cycle around the world. In Pakistan and other countries, these wastes are generally not exploited to be reused or recycled. Agro and marine waste contain cellulose, proteins and other valuable compounds to use in many important processes including the production of bio-plastic, bio-films and food application. People consume seafood and throw the outer shells of these fishes and shrimps or during pre-processing of fishes and shrimps their exoskeleton is being treated as waste and leftover, without knowing the potential this waste has. One of the major components this waste contain is Chitosan, which has multiple application one of which is application as bio-film. As fruit industry is on the verge of increasing the import/export volume, similarly the waste is also accumulating and increasing, considering the need the shelf life of these fruits and vegetables, a sustainable solution to preserve them is required, which can be achieve through chitosan made bio-films. The extraction of Chitosan is started with collection of shrimp’s shells and series of chemical treatments having three main steps including Demineralization, deproteinization and deacetylation. These steps involve treatment with HCl and NaOH dilute and concentrated subsequently. Test for the Chitosan include solubility in the presence of acetic acid and degree of deacetylation with titration. The chitosan can further utilize for the preparation of biofilm. The biofilm is made with acetic acid and essential oil which can be used on citric and non-citric fruits to increase the shelf life of fruits.
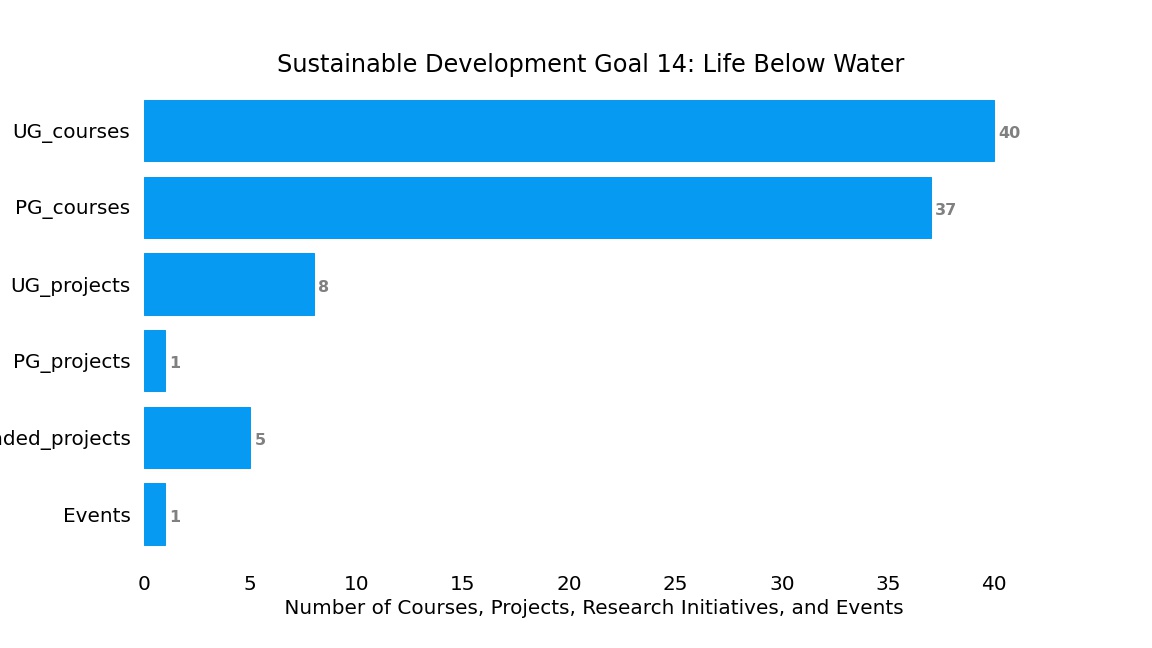
Activity Summary Graph
The following graph depicts the course offerings and other recent activities carried out at NED University of Engineering and Technology both at undergraduate (UG) and postgraduate (PG), relevant to the requirements of sustainable development goal 14. A brief description of the same follows.
Undergraduate Courses
Following is the list of relevant courses currently being offered in different undergraduate programmes of the University. The credit hour detail of the same can be found in the University’s Undergraduate Prospectus, available at https://www.neduet.edu.pk/prospectus.
| 1 | DS-406: Environmental Issues in Development |
| 2 | DS-408: Sustainability in Development |
| 3 | FD-430: Food Engineering Project |
| 4 | ME-420: Operations Management |
| 5 | ME-421: Gas Turbine |
| 6 | ME-425: Finite Element Analysis |
| 7 | ME-426: Plant Maintenance |
| 8 | ME-428: Health, Safety & Environment |
| 9 | ME-429: Water Treatment & Desalination |
| 10 | ME-430: Mechatronics |
| 11 | ME-431: Tribology |
| 12 | ME-432: Health, Safety and Environment |
| 13 | ME-435: Operations Management |
| 14 | ME-436: Mechanical Vibrations |
| 15 | ME-437: Machine Design and Vibration Lab |
| 16 | ME-438: AI and Internet of Things |
| 17 | MM-301: Corrosion: Protection and Prevention |
| 18 | MY-413: Corrosion Engineering |
| 19 | PE-202: Petroleum Geology |
| 20 | PE-210: Thermodynamics-I |
| 21 | TS-102: Textile Raw Materials-I |
| 22 | TS-108: Textile Raw Materials-II |
| 23 | TS-109: Introduction to Textiles |
| 24 | TS-119: Introduction to Textiles |
| 25 | TS-205: Pre-Spinning Processes |
| 26 | TS-206: Yarn Production Processes |
| 27 | TS-207: High Performance Fibres |
| 28 | TS-208: Weaving Preparatory Processes |
| 29 | TS-209: Colour Science |
| 30 | TS-233: Textile Testing-I |
| 31 | TS-245: Pre-treatment in Textiles |
| 32 | TS-341: Advanced Yarn Production Processes |
| 33 | TS-343: Weaving Mechanisms |
| 34 | TS-354: Knitting Technology |
| 35 | TS-356: Textile Dyeing |
| 36 | TS-358: Textile Printing |
| 37 | TS-361: Textile Testing-II |
| 38 | TS-455: Advanced Fabric Manufacturing Technique |
| 39 | TS-458: Project |
| 40 | TS-470: Technical Textiles |
Postgraduate Courses
Following is the list of relevant courses currently being offered in different postgraduate programmes of the University. The credit hour detail of the same can be found in the University’s Postgraduate Prospectus, available at https://www.neduet.edu.pk/prospectus.
| 1 | AR-626: Remote Sensing |
| 2 | BM-542: Finite Element Method |
| 3 | BM-553: Advanced Biomaterials |
| 4 | CE-5002: Thesis |
| 5 | CE-5016: Fundamentals of Environmental Laws for Construction Industr1 |
| 6 | CE-532: Foundation Engineering |
| 7 | CE-533: Soil Foundation D1namics |
| 8 | CE-538: Groundwater and Seepage |
| 9 | CE-539: Subsurface H1drolog1 |
| 10 | CE-579: Water Qualit1 Management |
| 11 | CE-580: Applied H1drolog1 |
| 12 | CE-583: Groundwater Engineering |
| 13 | CH-5002: Thesis |
| 14 | CH-517: Corrosion |
| 15 | C1-511: Research Methodolog1 |
| 16 | C1-512: Drug and Heteroc1clic Chemistr1 |
| 17 | EE-5002: Thesis |
| 18 | EN-5002: Thesis |
| 19 | EN-502: Environmental Applied Science |
| 20 | EN-508: Environment Impact Assessment |
| 21 | EN-510: Process D1namics in Environmental S1stem |
| 22 | EN-511: Environmental Management |
| 23 | EN-513: Industrial Waste Treatment and Disposal |
| 24 | EN-514: Water Resources Management |
| 25 | EN-515: Air Pollution and Control |
| 26 | EN-518: Sustainable Development & Appropriate Technolog1 |
| 27 | EN-520: Marine Pollution and Control |
| 28 | EN-521: Special Topics in Environmental Engineering |
| 29 | EN-523: Anal1sis of Environmental Contaminants |
| 30 | EN-524: Wastewater Engineering |
| 31 | EN-525: Ph1sico Chemical Processes |
| 32 | EN-526: Solid Waste Management |
| 33 | EN-527: Environmental Health and Sanitation |
| 34 | EN-531: Environmental Qualit1 Management |
| 35 | EN-537: Water Qualit1 Management |
| 36 | EN-540: Health, Safet1 & Environmental Management |
| 37 | EN-541: Remote Sensing in Environmental Management |
Undergraduate projects
Following is the list of relevant Final Year Design Projects (FYDP) thesis carried out at undergraduate level in the University.
- Effectiveness of Bio-waste for the Removal of Oil from Wastewater
- Application of Bio-sorbents to Remove Organic and Inorganic Pollutants from Wastewater.
- Fabrication and design of solar based air purifier for improving air quality index
- Electric Power Generation using wind turbine by applying the concept of Doubly Fed Induction Generator (DFIG) where constant power output is achieved in variable wind conditions
- Water Trash Collecting Robot Using Wireless Communication
- Smart Helmet
- Home automation and Home security using AI
- Designing of ion exchange membrane module for caustic recovery from mercerization waste
Postgraduate Projects
Following is the list of relevant thesis carried out at postgraduate level in the University.
- Classification of various furniture items from indoor and outdoor 3D point clouds (IE)
Externally Funded Research Projects
Following is the list of relevant research projects funded by external agencies, which are currently being carried out in the University.
- Solar powered atmospheric plasma system for treatment of contaminated wastewater
- Smart potable water harvesting grid for adaptive social capacity in varying humidity and insolation regions
- Development of Energy efficient housing design
- Smart Potable Water Harvesting Grid for Adaptive Social Capacity in varying Humidity and Insolation Regions
Events and Curricular Activities
A number of relevant activities are being carried out from time to time in the University, both by the departmental administrations and the students. Some significant activities are as follows.
- The session on Reuse of Plastic Bottle for Plantation
